IDA Pro MCP
Enabling Model Context Protocol server integration with IDA Pro for collaborative reverse engineering.
Key Features
Use Cases
README
IDA Pro MCP
Simple MCP Server to allow vibe reversing in IDA Pro.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/6ebeaa92-a9db-43fa-b756-eececce2aca0
The binaries and prompt for the video are available in the mcp-reversing-dataset repository.
Available functionality:
check_connection(): Check if the IDA plugin is running.get_metadata(): Get metadata about the current IDB.get_function_by_name(name): Get a function by its name.get_function_by_address(address): Get a function by its address.get_current_address(): Get the address currently selected by the user.get_current_function(): Get the function currently selected by the user.convert_number(text, size): Convert a number (decimal, hexadecimal) to different representations.list_functions_filter(offset, count, filter): List matching functions in the database (paginated).list_functions(offset, count): List all functions in the database (paginated).list_globals_filter(offset, count, filter): List matching globals in the database (paginated, filtered).list_globals(offset, count): List all globals in the database (paginated).list_imports(offset, count): List all imported symbols with their name and module (paginated).list_strings_filter(offset, count, filter): List matching strings in the database (paginated, filtered).list_strings(offset, count): List all strings in the database (paginated).list_local_types(): List all Local types in the database.decompile_function(address): Decompile a function at the given address.disassemble_function(start_address): Get assembly code for a function (API-compatible with older IDA builds).get_xrefs_to(address): Get all cross references to the given address.get_xrefs_to_field(struct_name, field_name): Get all cross references to a named struct field (member).get_callees(function_address): Get all the functions called (callees) by the function at function_address.get_callers(function_address): Get all callers of the given address.get_entry_points(): Get all entry points in the database.set_comment(address, comment): Set a comment for a given address in the function disassembly and pseudocode.rename_local_variable(function_address, old_name, new_name): Rename a local variable in a function.rename_global_variable(old_name, new_name): Rename a global variable.set_global_variable_type(variable_name, new_type): Set a global variable's type.patch_address_assembles(address, instructions): .get_global_variable_value_by_name(variable_name): Read a global variable's value (if known at compile-time).get_global_variable_value_at_address(address): Read a global variable's value by its address (if known at compile-time).rename_function(function_address, new_name): Rename a function.set_function_prototype(function_address, prototype): Set a function's prototype.declare_c_type(c_declaration): Create or update a local type from a C declaration.set_local_variable_type(function_address, variable_name, new_type): Set a local variable's type.get_stack_frame_variables(function_address): Retrieve the stack frame variables for a given function.get_defined_structures(): Returns a list of all defined structures.analyze_struct_detailed(name): Detailed analysis of a structure with all fields.get_struct_at_address(address, struct_name): Get structure field values at a specific address.get_struct_info_simple(name): Simple function to get basic structure information.search_structures(filter): Search for structures by name pattern.rename_stack_frame_variable(function_address, old_name, new_name): Change the name of a stack variable for an IDA function.create_stack_frame_variable(function_address, offset, variable_name, type_name): For a given function, create a stack variable at an offset and with a specific type.set_stack_frame_variable_type(function_address, variable_name, type_name): For a given disassembled function, set the type of a stack variable.delete_stack_frame_variable(function_address, variable_name): Delete the named stack variable for a given function.read_memory_bytes(memory_address, size): Read bytes at a given address.data_read_byte(address): Read the 1 byte value at the specified address.data_read_word(address): Read the 2 byte value at the specified address as a WORD.data_read_dword(address): Read the 4 byte value at the specified address as a DWORD.data_read_qword(address): Read the 8 byte value at the specified address as a QWORD.data_read_string(address): Read the string at the specified address.
Unsafe functions (--unsafe flag required):
dbg_get_registers(): Get all registers and their values. This function is only available when debugging.dbg_get_call_stack(): Get the current call stack.dbg_list_breakpoints(): List all breakpoints in the program.dbg_start_process(): Start the debugger, returns the current instruction pointer.dbg_exit_process(): Exit the debugger.dbg_continue_process(): Continue the debugger, returns the current instruction pointer.dbg_run_to(address): Run the debugger to the specified address.dbg_set_breakpoint(address): Set a breakpoint at the specified address.dbg_step_into(): Step into the current instruction.dbg_step_over(): Step over the current instruction.dbg_delete_breakpoint(address): Delete a breakpoint at the specified address.dbg_enable_breakpoint(address, enable): Enable or disable a breakpoint at the specified address.
Prerequisites
- Python (3.11 or higher)
- Use
idapyswitchto switch to the newest Python version
- Use
- IDA Pro (8.3 or higher, 9 recommended), IDA Free is not supported
- Supported MCP Client (pick one you like)
- Cline
- Roo Code
- Claude
- Cursor
- VSCode Agent Mode
- Windsurf
- Other MCP Clients: Run
ida-pro-mcp --configto get the JSON config for your client.
Installation
Install the latest version of the IDA Pro MCP package:
pip uninstall ida-pro-mcp
pip install https://github.com/mrexodia/ida-pro-mcp/archive/refs/heads/main.zip
Configure the MCP servers and install the IDA Plugin:
ida-pro-mcp --install
Important: Make sure you completely restart IDA/Visual Studio Code/Claude for the installation to take effect. Claude runs in the background and you need to quit it from the tray icon.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/65ed3373-a187-4dd5-a807-425dca1d8ee9
Note: You need to load a binary in IDA before the plugin menu will show up.
Prompt Engineering
LLMs are prone to hallucinations and you need to be specific with your prompting. For reverse engineering the conversion between integers and bytes are especially problematic. Below is a minimal example prompt, feel free to start a discussion or open an issue if you have good results with a different prompt:
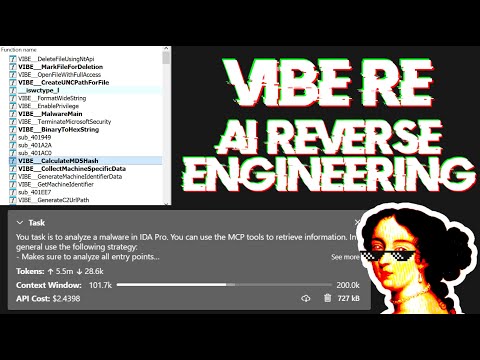
Your task is to analyze a crackme in IDA Pro. You can use the MCP tools to retrieve information. In general use the following strategy:
- Inspect the decompilation and add comments with your findings
- Rename variables to more sensible names
- Change the variable and argument types if necessary (especially pointer and array types)
- Change function names to be more descriptive
- If more details are necessary, disassemble the function and add comments with your findings
- NEVER convert number bases yourself. Use the convert_number MCP tool if needed!
- Do not attempt brute forcing, derive any solutions purely from the disassembly and simple python scripts
- Create a report.md with your findings and steps taken at the end
- When you find a solution, prompt to user for feedback with the password you found
This prompt was just the first experiment, please share if you found ways to improve the output!
Live stream discussing prompting and showing some real-world malware analysis:
Tips for Enhancing LLM Accuracy
Large Language Models (LLMs) are powerful tools, but they can sometimes struggle with complex mathematical calculations or exhibit "hallucinations" (making up facts). Make sure to tell the LLM to use the conver_number MCP and you might also need math-mcp for certain operations.
Another thing to keep in mind is that LLMs will not perform well on obfuscated code. Before trying to use an LLM to solve the problem, take a look around the binary and spend some time (automatically) removing the following things:
- String encryption
- Import hashing
- Control flow flattening
- Code encryption
- Anti-decompilation tricks
You should also use a tool like Lumina or FLIRT to try and resolve all the open source library code and the C++ STL, this will further improve the accuracy.
SSE Transport & Headless MCP
You can run an SSE server to connect to the user interface like this:
uv run ida-pro-mcp --transport http://127.0.0.1:8744/sse
After installing idalib you can also run a headless SSE server:
uv run idalib-mcp --host 127.0.0.1 --port 8745 path/to/executable
Note: The idalib feature was contributed by Willi Ballenthin.
Manual Installation
Note: This section is for LLMs and power users who need detailed installation instructions.
Manual MCP Server Installation (Cline/Roo Code)
To install the MCP server yourself, follow these steps:
- Install uv globally:
- Windows:
pip install uv - Linux/Mac:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
- Windows:
- Clone this repository, for this example
C:\MCP\ida-pro-mcp. - Navigate to the Cline/Roo Code MCP Servers configuration (see screenshot).
- Click on the Installed tab.
- Click on Configure MCP Servers, which will open
cline_mcp_settings.json. - Add the
ida-pro-mcpserver:
{
"mcpServers": {
"github.com/mrexodia/ida-pro-mcp": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"c:\\MCP\\ida-pro-mcp",
"run",
"server.py",
"--install-plugin"
],
"timeout": 1800,
"disabled": false
}
}
}
To check if the connection works you can perform the following tool call:
<use_mcp_tool>
<server_name>github.com/mrexodia/ida-pro-mcp</server_name>
<tool_name>check_connection</tool_name>
<arguments></arguments>
</use_mcp_tool>
IDA Plugin installation
The IDA Pro plugin will be installed automatically when the MCP server starts. If you disabled the --install-plugin option, use the following steps:
- Copy (not move)
src/ida_pro_mcp/mcp-plugin.pyin your plugins folder (%appdata%\Hex-Rays\IDA Pro\pluginson Windows). - Open an IDB and click
Edit -> Plugins -> MCPto start the server.
Comparison with other MCP servers
There are a few IDA Pro MCP servers floating around, but I created my own for a few reasons:
- Installation should be fully automated.
- The architecture of other plugins make it difficult to add new functionality quickly (too much boilerplate of unnecessary dependencies).
- Learning new technologies is fun!
If you want to check them out, here is a list (in the order I discovered them):
- https://github.com/taida957789/ida-mcp-server-plugin (SSE protocol only, requires installing dependencies in IDAPython).
- https://github.com/fdrechsler/mcp-server-idapro (MCP Server in TypeScript, excessive boilerplate required to add new functionality).
- https://github.com/MxIris-Reverse-Engineering/ida-mcp-server (custom socket protocol, boilerplate).
Feel free to open a PR to add your IDA Pro MCP server here.
Development
Adding new features is a super easy and streamlined process. All you have to do is add a new @jsonrpc function to mcp-plugin.py and your function will be available in the MCP server without any additional boilerplate! Below is a video where I add the get_metadata function in less than 2 minutes (including testing):
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/951de823-88ea-4235-adcb-9257e316ae64
To test the MCP server itself:
uv run mcp dev src/ida_pro_mcp/server.py
This will open a web interface at http://localhost:5173 and allow you to interact with the MCP tools for testing.
For testing I create a symbolic link to the IDA plugin and then POST a JSON-RPC request directly to http://localhost:13337/mcp. After enabling symbolic links you can run the following command:
uv run ida-pro-mcp --install
Generate the changelog of direct commits to main:
git log --first-parent --no-merges 1.2.0..main "--pretty=- %s"
Star History
Repository Owner
User
Repository Details
Programming Languages
Tags
Topics
Join Our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest AI tools, news, and offers by subscribing to our weekly newsletter.
Related MCPs
Discover similar Model Context Protocol servers

JADX-AI-MCP
Automated AI-powered APK analysis via Model Context Protocol.
JADX-AI-MCP is a fully automated server and plugin for integrating Model Context Protocol (MCP) with JADX for the purpose of analyzing Android APKs using large language models such as Claude. It streamlines vulnerability discovery, reverse engineering, and static analysis by leveraging LLMs in conjunction with established tools. The project facilitates real-time code review and efficient collaboration between AI and human analysts.
- ⭐ 637
- MCP
- zinja-coder/jadx-ai-mcp

Kanboard MCP Server
MCP server for seamless AI integration with Kanboard project management.
Kanboard MCP Server is a Go-based server implementing the Model Context Protocol (MCP) for integrating AI assistants with the Kanboard project management system. It enables users to manage projects, tasks, users, and workflows in Kanboard directly via natural language commands through compatible AI tools. With built-in support for secure authentication and high performance, it facilitates streamlined project operations between Kanboard and AI-powered clients like Cursor or Claude Desktop. The server is configurable and designed for compatibility with MCP standards.
- ⭐ 15
- MCP
- bivex/kanboard-mcp

GitHub MCP Server
Connect AI tools directly to GitHub for repository, issue, and workflow management via natural language.
GitHub MCP Server enables AI tools such as agents, assistants, and chatbots to interact natively with the GitHub platform. It allows these tools to access repositories, analyze code, manage issues and pull requests, and automate workflows using the Model Context Protocol (MCP). The server supports integration with multiple hosts, including VS Code and other popular IDEs, and can operate both remotely and locally. Built for developers seeking to enhance AI-powered development workflows through seamless GitHub context access.
- ⭐ 24,418
- MCP
- github/github-mcp-server

solvitor-mcp
A Rust-based MCP server for extracting Solana smart contract IDL via the Solvitor API.
solvitor-mcp is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server built in Rust for seamless interaction with the Solvitor API. It allows users to extract Interface Definition Language (IDL) files from closed-source Solana smart contracts using reverse engineering techniques. By exposing a 'decode' tool, it simplifies access to program metadata and supports both 'anchor' and 'native' Solana programs. Integration is straightforward and can be customized with user API keys for secure access.
- ⭐ 2
- MCP
- Adeptus-Innovatio/solvitor-mcp

Code Declaration Lookup MCP Server
Fast, language-agnostic code declaration search and lookup server via MCP.
Provides a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that indexes code declarations using universal ctags and SQLite with FTS5 full-text search. Offers search and listing functionality for functions, classes, structures, enums, and other code elements across any language supported by ctags. Enables seamless integration with coding agents for dynamic indexing, respects .gitignore, and supports ctags file ingestion and management.
- ⭐ 2
- MCP
- osinmv/function-lookup-mcp

Semgrep MCP Server
A Model Context Protocol server powered by Semgrep for seamless code analysis integration.
Semgrep MCP Server implements the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to enable efficient and standardized communication for code analysis tasks. It facilitates integration with platforms like LM Studio, Cursor, and Visual Studio Code, providing both Docker and Python (PyPI) deployment options. The tool is now maintained in the main Semgrep repository with continued updates, enhancing compatibility and support across developer tools.
- ⭐ 611
- MCP
- semgrep/mcp
Didn't find tool you were looking for?