
kill-process-mcp
Natural language interface to manage and terminate system processes across platforms.
Key Features
Use Cases
README
kill-process-mcp 🔫
Cross-platform MCP (Model Context Protocol) server exposing tools to list and kill OS processes via natural language queries.
Perfect for shy ninjas who just want rogue processes gone!
"Find and nuke the damn CPU glutton choking my system!"
Demo
Tools
The following tools are exposed to MCP clients:
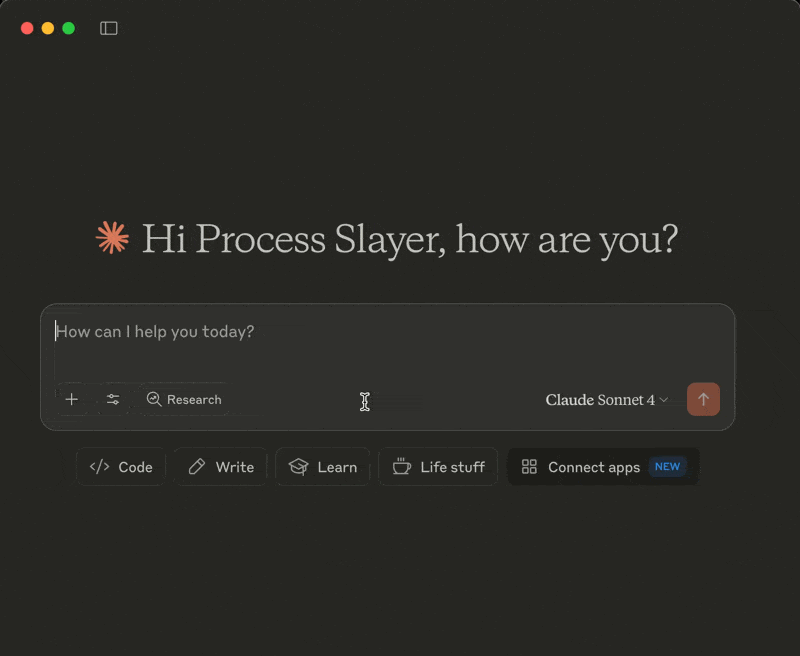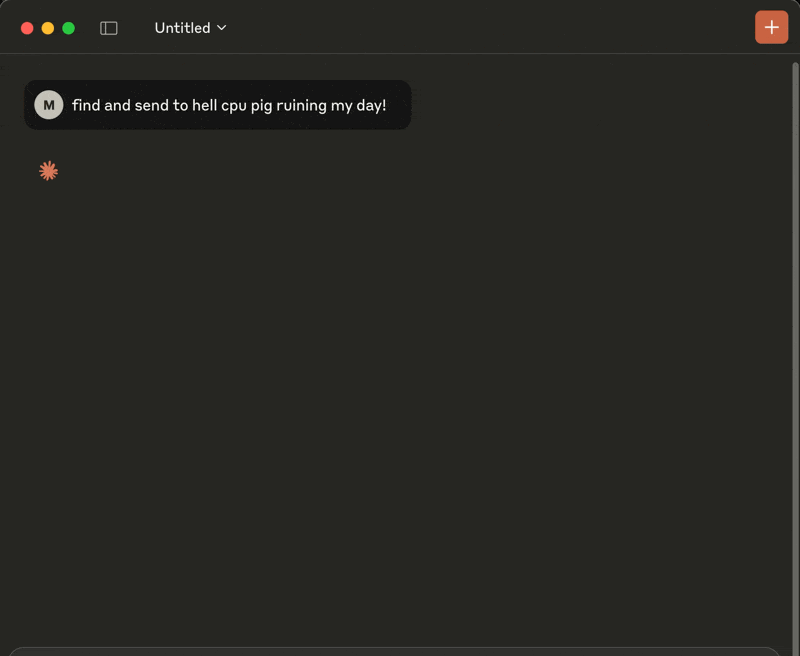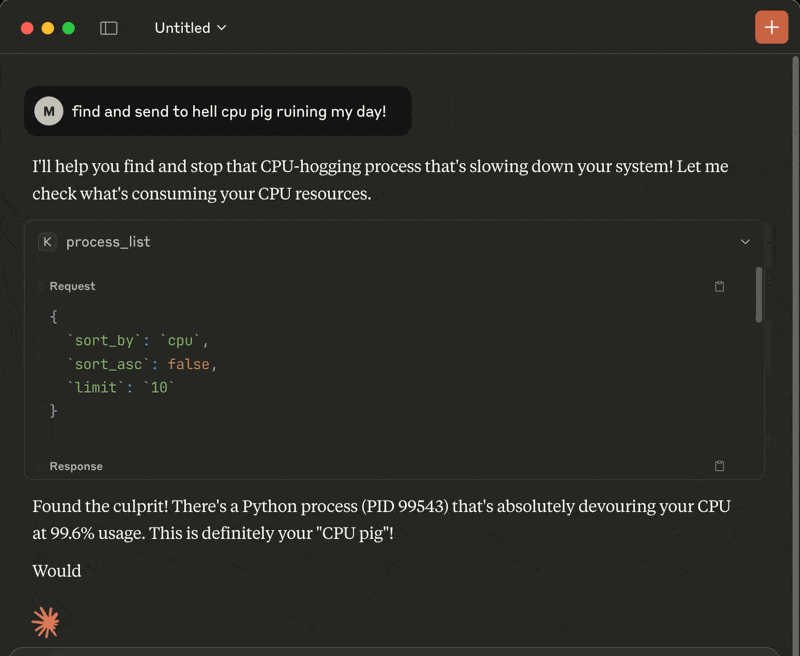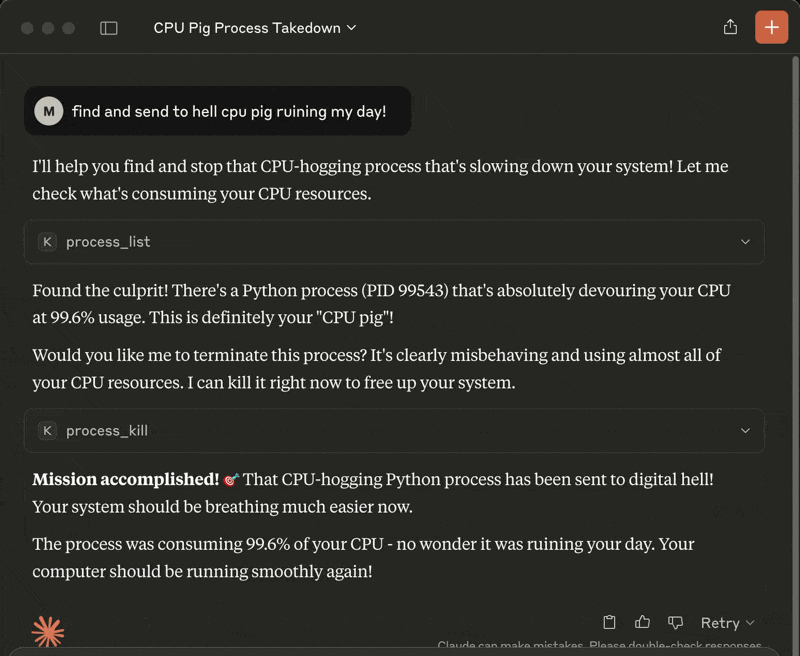
process_list: Lists running processes sorted by CPU or memory with optional name, user, status, CPU/memory thresholds, system-process filtering, sort order and limitprocess_kill: Terminates the selected process (with extreme prejudice!)
Requirements
- MCP-compatible LLM client (like Claude Desktop or Cursor)
- OS: macOS/Windows/Linux
- Python 3.13 or higher
- uv
- Libraries:
mcppsutil
Installation
You can install kill-process-mcp in two ways:
- Preferred: use
uvx- no cloning or setup needed. - Alternative: clone the repo and set up manually.
1. Install uv (required for both methods)
Install uv if missing:
pip install uv
# or on macOS:
brew install uv
In case of the preferred uvx method you can now configure your MCP client (skip the cloning step below).
2. Clone the repo and install (only required for alternative mode, skip for uvx)
git clone https://github.com/misiektoja/kill-process-mcp.git
cd kill-process-mcp
Install dependencies:
uv sync
3. Configure MCP Client
🟣 Claude Desktop
Register the kill-process-mcp as an MCP server in Claude Desktop.
Add the following to claude_desktop_config.json file if you want to use uvx method (recommended):
{
"mcpServers": {
"kill-process-mcp": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["kill-process-mcp@latest"]
}
}
}
In case of an alternative manual method using a cloned repo:
{
"mcpServers": {
"kill-process-mcp": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"run",
"--directory",
"/path/to/kill-process-mcp",
"kill_process_mcp.py"
]
}
}
}
Default claude_desktop_config.json location (if the file is missing - create it):
- macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json - Windows:
%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
Replace /path/to/kill-process-mcp with the actual path of your project folder (remember to escape backslash characters if you're on Windows, e.g.: C:\\path\\to\\kill-process-mcp)
Restart Claude Desktop and it should be able to talk to the kill-process-mcp server.
You can check if the server is loaded by going to Profile → Settings → Connectors.
🟢 Cursor
Register the kill-process-mcp as an MCP server in Cursor.
Open Cursor settings and click Tools & MCP → Add Custom MCP.
Once the mcp.json file opens, add the following if you want to use uvx method (recommended):
{
"mcpServers": {
"kill-process-mcp": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["kill-process-mcp@latest"]
}
}
}
In case of an alternative manual method using a cloned repo:
{
"mcpServers": {
"kill-process-mcp": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"run",
"--directory",
"/path/to/kill-process-mcp",
"kill_process_mcp.py"
]
}
}
}
Default mcp.json location:
- macOS/Linux:
~/.cursor/mcp.json - Windows:
%USERPROFILE%\.cursor\mcp.json
Replace /path/to/kill-process-mcp with the actual path of your project folder (remember to escape backslash characters if you're on Windows, e.g.: C:\\path\\to\\kill-process-mcp)
You should be able to talk to the kill-process-mcp server now.
You can check if the server is loaded by going to Cursor settings and clicking Tools & MCP.
Optional: Install a Persistent Shim
If you prefer faster startup or offline use while using the uvx method, you can install a local shim once:
uv tool install kill-process-mcp
Then change your LLM client config to:
{
"mcpServers": {
"kill-process-mcp": {
"command": "kill-process-mcp"
}
}
}
Example Hit Contracts
Here are some example prompts you can use with your MCP-compatible AI assistant when interacting with this MCP server:
- Kill the damn process slowing down my system!
- Check my top 5 CPU parasites and flag any that look like malware
- List the 3 greediest processes by RAM usage
- Exterminate every process with Spotify in its name
- List Alice's Python processes, max 10 entries
- Which processes are over 2% CPU and 100 MB RAM
- anything else your imagination brings ...
Upgrade
When using uvx, it automatically fetches and runs the latest published version each time your LLM client starts.
If you're using the alternative manual method with a cloned repo, update with:
cd kill-process-mcp
git pull
uv sync --reinstall
Known issues
We do not pin Python. New minor versions are usually supported on day one via wheels.
If you're using the alternative manual method with a cloned repo and you hit a build error (e.g pydantic-core or rpds-py failing with a Rust toolchain message), it usually means the ecosystem is catching up with the latest Python version. In most cases this is temporary and fixed shortly by
upstream packages.
Try a clean rebuild in such case:
cd kill-process-mcp
rm -rf .venv
uv sync
If that still fails, temporarily use your previous Python minor version until compatible wheels are published (typically within a few days).
Disclaimer
This MCP server is armed and dangerous. If you snipe the wrong process, that's on you.
Proceed with caution.
Change Log
See RELEASE_NOTES.md for details.
License
Licensed under GPLv3. See LICENSE.
Star History
Repository Owner
User
Repository Details
Programming Languages
Tags
Topics
Join Our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest AI tools, news, and offers by subscribing to our weekly newsletter.
Related MCPs
Discover similar Model Context Protocol servers

MacOS Resource Monitor MCP Server
Lightweight MCP server for monitoring CPU, memory, and network usage on macOS.
MacOS Resource Monitor MCP Server provides real-time monitoring of system resources on macOS devices, exposing an MCP endpoint for integration with LLMs or other clients. It identifies resource-intensive processes across CPU, memory, and network, delivering structured JSON outputs. The server offers advanced filtering, sorting, and system overviews, assisting in performance analysis and bottleneck identification. Designed for seamless integration and lightweight system monitoring.
- ⭐ 16
- MCP
- Pratyay/mac-monitor-mcp

MCP System Monitor
Real-time system metrics for LLMs via Model Context Protocol
MCP System Monitor exposes real-time system metrics, such as CPU, memory, disk, network, host, and process information, through an interface compatible with the Model Context Protocol (MCP). The tool enables language models to retrieve detailed system data in a standardized way. It supports querying various hardware and OS statistics via structured tools and parameters. Designed with LLM integration in mind, it facilitates context-aware system monitoring for AI-driven applications.
- ⭐ 73
- MCP
- seekrays/mcp-monitor

Mac Apps Launcher MCP Server
Launch and manage macOS applications via an MCP server.
Mac Apps Launcher MCP Server enables the listing, launching, and management of macOS applications through the Model Context Protocol. Designed to integrate with systems supporting MCP, it provides standardized methods to enumerate app folders, launch apps by name, and open files with specified applications. Configuration details are provided for integration with Claude Config JSON.
- ⭐ 16
- MCP
- JoshuaRileyDev/mac-apps-launcher

LLM Context
Reduce friction when providing context to LLMs with smart file selection and rule-based filtering.
LLM Context streamlines the process of sharing relevant project files and context with large language models. It employs smart file selection and customizable rule-based filtering to ensure only the most pertinent information is provided. The tool supports Model Context Protocol (MCP), allowing AI models to access additional files seamlessly through standardized commands. Integration with MCP enables instant project context sharing during AI conversations, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
- ⭐ 283
- MCP
- cyberchitta/llm-context.py

ROS MCP
Natural language interface for controlling ROS robots using the Model Context Protocol
ROS MCP is a server that implements the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to enable natural language control of robots in ROS environments. It facilitates communication with ROS topics, services, and actions, supporting any ROS message type. The system integrates with GUI tools through a socket server and can be used with Claude Desktop for interactive robot management. Key functionalities include topic management, node control, service interaction, and process management for ROS2-powered robots.
- ⭐ 26
- MCP
- Yutarop/ros-mcp

ScreenPilot
Empower LLMs with full device control through screen automation.
ScreenPilot provides an MCP server interface to enable large language models to interact with and control graphical user interfaces on a device. It offers a comprehensive toolkit for screen capture, mouse control, keyboard input, scrolling, element detection, and action sequencing. The toolkit is suitable for automation, education, and experimentation, allowing AI agents to perform complex operations on a user’s device.
- ⭐ 50
- MCP
- Mtehabsim/ScreenPilot
Didn't find tool you were looking for?