
LLDB-MCP
AI-assisted debugging with LLDB via Model Context Protocol integration
Key Features
Use Cases
README
LLDB-MCP
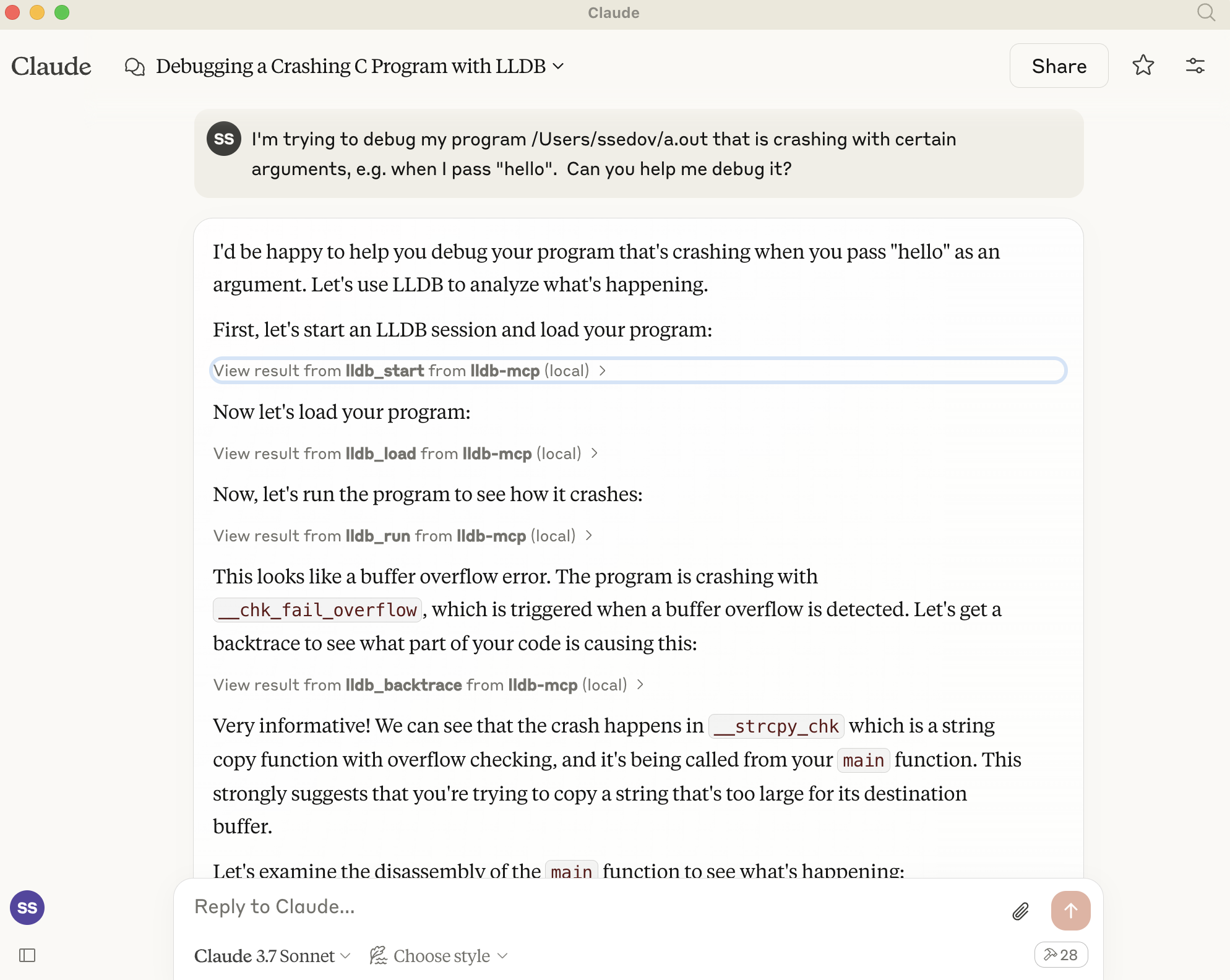
See it in acton here, automatically debugging a buffer overflow: https://x.com/full_duplex/status/1904770477698277847
Overview
LLDB-MCP is a tool that integrates the LLDB debugger with Claude's Model Context Protocol (MCP). This integration allows Claude to start, control, and interact with LLDB debugging sessions directly, enabling AI-assisted debugging workflows.
The tool provides a comprehensive set of commands for working with LLDB, including:
- Starting and managing LLDB sessions
- Loading programs for debugging
- Setting breakpoints and watchpoints
- Controlling program execution
- Examining memory, registers, and variables
- Analyzing stack traces and program state
Features
- Create and manage multiple LLDB debugging sessions
- Load executables and attach to running processes
- Load core dump files for post-mortem analysis
- Execute arbitrary LLDB commands
- Fine-grained control over program execution
- Memory examination and disassembly
- Thread and stack frame inspection
Installation
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/stass/lldb-mcp.git cd lldb-mcp -
Install dependencies:
pip install mcp -
Configure Claude to use the LLDB-MCP server:
- Open the Claude desktop app configuration
- Add the following to your MCP configuration:
json"mcpServers": { "lldb-mcp": { "command": "python3", "args": ["/path/to/lldb-mcp/lldb_mcp.py"], "disabled": false } }
Usage
Once installed and configured, you can interact with LLDB through Claude using natural language.
Basic Workflow
- Start a new LLDB session
- Load a program
- Set breakpoints
- Run the program
- Inspect variables and memory
- Control execution (continue, step, next, etc.)
- Terminate the session when done
Example Commands
Here are some examples of how to interact with LLDB-MCP through Claude:
- "Start a new LLDB session"
- "Load the program '/path/to/executable'"
- "Set a breakpoint at main"
- "Run the program"
- "Show backtrace"
- "Print the value of variable 'count'"
- "Step over the next line"
- "Examine memory at address 0x1000"
- "Show register values"
- "Continue execution"
- "Kill the process"
- "Terminate the LLDB session"
Supported Commands
Session Management
lldb_start: Start a new LLDB sessionlldb_terminate: Terminate an LLDB sessionlldb_list_sessions: List all active LLDB sessions
Program Loading
lldb_load: Load a program into LLDBlldb_attach: Attach to a running processlldb_load_core: Load a core dump file
Execution Control
lldb_run: Run the loaded programlldb_continue: Continue program executionlldb_step: Step to next line or instructionlldb_next: Step over function callslldb_finish: Execute until the current function returnslldb_kill: Kill the running process
Breakpoints and Watchpoints
lldb_set_breakpoint: Set a breakpointlldb_breakpoint_list: List all breakpointslldb_breakpoint_delete: Delete a breakpointlldb_watchpoint: Set a watchpoint on a variable or memory address
Inspection
lldb_backtrace: Show call stacklldb_print: Print value of expressionlldb_examine: Examine memorylldb_info_registers: Display registerslldb_frame_info: Get detailed information about a stack framelldb_disassemble: Disassemble codelldb_process_info: Get information about the current process
Thread Management
lldb_thread_list: List all threads in the current processlldb_thread_select: Select a specific thread
Miscellaneous
lldb_command: Execute an arbitrary LLDB commandlldb_expression: Evaluate an expression in the current framelldb_help: Get help for LLDB commands
Example program
example/overflow.c contains an example C program that causes buffer overflow with certain arguments.
Compile it using cc overflow.c and ask Claude to debug the issue with the resulting program:
I'm trying to debug my program a.out that is crashing with certain arguments, e.g. when I pass "hello".
Can you help me debug it?
Debugging Tips
- Use
lldb_commandwhen you need to execute LLDB commands that don't have a dedicated function - Enable debug mode with
--debugflag when starting the server for detailed logging - Sessions are automatically cleaned up when the server shuts down
- Each session has a unique ID - make sure to use the correct ID when executing commands
Requirements
- Python 3.7+
- LLDB installed on the system
- Claude desktop app with MCP support
Troubleshooting
- If LLDB commands are timing out, check that LLDB is installed correctly
- Verify the path to LLDB when starting a new session
- Check for permission issues when attaching to processes
- Review debug logs if commands aren't executing correctly
License
BSD 2-clause
Star History
Repository Owner
User
Repository Details
Programming Languages
Join Our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest AI tools, news, and offers by subscribing to our weekly newsletter.
Related MCPs
Discover similar Model Context Protocol servers

Lucidity MCP
Intelligent prompt-based code quality analysis for AI coding assistants.
Lucidity MCP is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that empowers AI coding assistants to deliver high-quality code through intelligent, prompt-driven analysis. It offers comprehensive detection of code issues across multiple quality dimensions, providing structured and actionable feedback. With language-agnostic capabilities, extensible framework, and flexible transport options, Lucidity MCP seamlessly integrates into developer workflows and AI systems.
- ⭐ 72
- MCP
- hyperb1iss/lucidity-mcp

VideoDB Agent Toolkit
AI Agent toolkit that exposes VideoDB context to LLMs with MCP support
VideoDB Agent Toolkit provides tools for exposing VideoDB context to large language models (LLMs) and agents, enabling integration with AI-driven IDEs and chat agents. It automates context generation, metadata management, and discoverability by offering structured context files like llms.txt and llms-full.txt, and standardized access via the Model Context Protocol (MCP). The toolkit ensures synchronization of SDK versions, comprehensive documentation, and best practices for seamless AI-powered workflows.
- ⭐ 43
- MCP
- video-db/agent-toolkit

Unity MCP
AI-powered game development assistant bridging MCP and Unity.
Unity MCP serves as an AI-powered assistant for game developers, acting as a bridge between MCP clients and the Unity engine. It enables natural chat-based interactions to perform various development tasks using large language models from multiple providers. The system offers tools for code assistance, debugging, and flexible deployment options, supporting both local and remote workflows. Its extensibility allows for the creation of custom MCP tools to enhance developer productivity in the Unity environment.
- ⭐ 510
- MCP
- IvanMurzak/Unity-MCP

Modbus MCP Server
Standardizes Modbus data for seamless AI integration via the Model Context Protocol.
Modbus MCP Server provides an MCP-compliant interface that standardizes and contextualizes Modbus device data for use with AI agents and industrial IoT systems. It supports flexible Modbus connections over TCP, UDP, or serial interfaces and offers a range of Modbus tools for reading and writing registers and coils. With customizable prompts and structured tool definitions, it enables natural language-driven interactions and analysis of Modbus data within AI workflows. The solution is designed to ensure interoperability and easy configuration within MCP-compatible environments.
- ⭐ 18
- MCP
- kukapay/modbus-mcp

QGISMCP
Integrate QGIS with Claude AI via Model Context Protocol
QGISMCP connects QGIS to Claude AI through the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling seamless two-way communication between the GIS platform and the AI assistant. It features a QGIS plugin that sets up a socket server and a dedicated MCP server for processing commands, facilitating tasks such as project manipulation, layer management, and Python code execution directly from Claude. This integration empowers users to streamline project creation, layer loading, and advanced automation within QGIS through AI-driven interaction.
- ⭐ 691
- MCP
- jjsantos01/qgis_mcp

GhidraMCP
AI-powered binary analysis through Model Context Protocol integration with Ghidra
GhidraMCP is a Ghidra plugin that implements the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling seamless connectivity between Ghidra and AI-powered assistants for advanced binary analysis. It allows users to interact with binaries using natural language, automate security and code analysis, and retrieve detailed program insights through a socket-based architecture. The plugin offers functions for exploring binary structures, analyzing memory layouts, and identifying vulnerabilities, providing a flexible and efficient reverse engineering workflow.
- ⭐ 77
- MCP
- 13bm/GhidraMCP
Didn't find tool you were looking for?