
MayaMCP
MCP server enabling natural language control of Autodesk Maya.
Key Features
Use Cases
README
Maya MCP
Model Context Protocol (MCP) server implementation for Autodesk Maya
Tested with Maya 2023, 2025.
v0.2.0
This project enables AI assistant clients like Claude Desktop to control Autodesk Maya through natural language using the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
This is early days for Maya MCP server and has a minimal set of functionality. It's really the architecture design and simplicity that has been the initial focus.
Here is a list of some of the tools registered with Maya MCP.
Basic Tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| list_objects_by_type | Get a list of objects in the scene. Use filter_by to filter for certain objects such as "cameras", "lights", "materials", or "shapes". |
| create_object | Create an object in the Maya scene. Object types available are cube, cone, sphere, cylinder, camera, spotLight, pointLight, directionalLight. |
| get_object_attributes | Get a list of attributes on a Maya object. |
| set_object_attributes | Set an object's attribute with a specific value. |
| scene_new | Create a new scene in Maya. Use the force argument to force a new scene when an existing scene is loaded and has been modified. |
| scene_open | Load in a scene into Maya. |
| scene_save | Save the current scene. If the filename is not specified, it will save it as its current name. |
| select_object | Select an object in the scene. |
Advanced Modeling Tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| create_advanced_model | Create complex 3D models like cars, trees, buildings, cups, and chairs with detailed parameters. |
| mesh_operations | Perform modeling operations such as extrude, bevel, subdivide, boolean, combine, bridge, and split. |
| create_material | Create and assign materials with various types (lambert, phong, wood, marble, chrome, glass, etc.) |
| create_curve | Generate NURBS curves for various shapes (line, circle, spiral, helix, star, gear, etc.) |
| curve_modeling | Create geometry using curve-based modeling techniques (extrude, loft, revolve, sweep, etc.) |
| organize_objects | Organize objects through grouping, parenting, layout, alignment, and distribution. |
| generate_scene | Generate complete 3D scenes with multiple objects (city, forest, living room, office, park) |
Installation
Maya MCP server is designed so there is only an MCP server and doesn't require anything to be installed within Maya. This is helpful since you can easily use different versions of Maya and not have to worry about coordinating version changes. This is done by taking advantage of the default Command Port Maya opens up for MEL scripting.
MCP requires Python 3.10 or greater. Currently using pip as the package requirements are minimal. To install the virtual environment:
- download this project
- Create a virtual env using Python 3.10+ in the project directory.
python -m venv .venv - activate the virtual environment
- Windows:
.venv\Scripts\activate.bat - Mac/Linux:
source .venv\bin\activate.sh
- Windows:
pip install -r requirements.txt
As stated, there is nothing to install for Maya.
MCP Client Configuration
Depending on which MCP Client you're using, the configuration file location differs. For Anthopic Claude Desktop, go to File -> Settings -> Developer Tab and press the Edit Config button. This will bring up the file finder in the directory location of the JSON config file.
Next you need to edit the config JSON file by hand using a text editor. Make sure to use full file paths.
{
"mcpServers": {
"MayaMCP": {
"command": "[FULL PATH TO MayaMCP PROJECT]/.venv/Scripts/python.exe",
"args": [
"[FULL PATH TO MayaMCP PROJECT]/src/maya_mcp_server.py"
]
}
}
}
Once the changes have been made, restart Claude Desktop (use Exit menu item instead of just closing the window). In the Developers Tab, you will now see the Maya MCP server listed.
In Claude Desktop, you can verify the Maya MCP tools are available. Press the  button and a detailed popup will appear.
button and a detailed popup will appear.

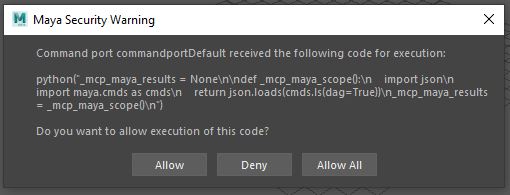
Maya Communications
When the Maya MCP server first attempts to communicate with Maya, you will get this popup within Maya. Please click "Allow All" to allow for ongoing communication between the MCP server and Maya. This will need to be done each Maya session.
Developer Notes
The Maya MCP Server module was designed to be easily modified in a non-intrusive way. This is done by having the Maya Python code reside in the MCP server and sent to Maya's command port for execution. The results are sent back to the server and processed.
The default Maya command port runs MEL so the Python code is modified to run within MEL function call to the Python interpreter. There is also some limits such as multi-line Python code can't have any returned results. So, each command creates two connections to Maya. First to run the operation and save the results. The second connection then to read back the results.
To help minimize populating the namespace in the Maya global Python interpreter, functions and variables sent to Maya will be scoped to start with mcp_maya*. Each of the Maya tools are scoped into a function named _mcp_maya_scope(). The results are assigned to the variable _mcp_maya_results. This way should significantly reduce the possibility of name collisions.
There is a bit of elegance to this design. You basically can just add the Python file, restart the MCP Client and Maya MCP server and go. You don't need to integrate the operations on both the Maya MCP server and Maya itself. The code you add is only Maya specific Python and doesn't need to add any MCP decorators. This is a much better design to grow and adapt to different installations instead of having a fixed set of tools.
The Maya MCP server was built using the low-level Python MCP module. This was necessary to allow for dynamically defining all of the tools at run time. The tool function signatures are captured dynamically at the start of the server.
Adding New Tools
It is easy to add new tools to Maya MCP. You don't need to change any of the existing code. All you need to do is add a single tool command Python file to the mayatools/thirdparty directory. The tool itself will run in Maya so it will have access to all of the Maya Python modules. There are a few programmer notes in the design of the tool.
- The name of the Python file and the function name must be the same. Make sure it is unique.
- The Python function will be loaded by both the server and Maya. Any code outside of the function must be able to be loaded into standalone Python. Meaning any imports such as maya.cmds should be done in the scope of the function. The MCP server loads the function so it can inspect the function signature to send the information to MCP Client via JSON-RPC.
- The function signature will be parsed and must include any types in the function argument annotation.
- When your function is sent to Maya, it will be scoped within am _mcp_maya_scope function. This provides a number of benefits. The functions sent to Maya will not polute the Python global space too much running in Maya. Plus, any exceptions thrown will be caught and returned back to the MCP Client as errors.
- Generally, you want to return either a list or dictionary or throw an exception when there is an error.
- Name your function and arguments appropriately so the LLM can understand the operation. Include a function doc string.
- Default arguments are good.
- Error checking is good so error messages can provide better failed explanations.
I recommend looking at the existing Maya tools in this project as examples.
Testing
Currently Maya MCP has only been tested on Windows. Should work on both Linux and Mac as everything is using standard Python.
Future Ideas
It's early days for MCP and there is a lot to improve. Here are some ideas.
- Expose more functionality.
- Improve using prompt engineering, particularly describing Maya's usage and data relationships.
- Everything is registered as tools, allow for resources and prompts.
- It could be possible to find any plugins within Maya that has MCP tools. Maybe something like looking at the PYTHONPATH within Maya with any directory named MCP. All of those could be inspected and then provided back to the MCP Client.
License
MIT
Links
Important Note
This project was done on my personal time and equipment to learn about MCP. The project is not affiliated with my current employer and does not represent their work or interests.
Star History
Repository Owner
User
Repository Details
Programming Languages
Tags
Join Our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest AI tools, news, and offers by subscribing to our weekly newsletter.
Related MCPs
Discover similar Model Context Protocol servers

awslabs/mcp
Specialized MCP servers for seamless AWS integration in AI and development environments.
AWS MCP Servers is a suite of specialized servers implementing the open Model Context Protocol (MCP) to bridge large language model (LLM) applications with AWS services, tools, and data sources. It provides a standardized way for AI assistants, IDEs, and developer tools to access up-to-date AWS documentation, perform cloud operations, and automate workflows with context-aware intelligence. Featuring a broad catalog of domain-specific servers, quick installation for popular platforms, and both local and remote deployment options, it enhances cloud-native development, infrastructure management, and workflow automation for AI-driven tools. The project includes Docker, Lambda, and direct integration instructions for environments such as Amazon Q CLI, Cursor, Windsurf, Kiro, and VS Code.
- ⭐ 6,220
- MCP
- awslabs/mcp

blender-mcp
Seamless integration between Blender and Claude AI using the Model Context Protocol.
BlenderMCP enables direct interaction between Blender and Claude AI by leveraging the Model Context Protocol (MCP). It allows users to create, manipulate, and inspect 3D scenes in Blender through natural language commands sent to Claude, which communicates with Blender via a custom socket server and an addon. The solution features two-way communication, object and material manipulation, code execution within Blender, and easy integration with tools like Cursor, Visual Studio Code, and Claude for Desktop.
- ⭐ 13,092
- MCP
- ahujasid/blender-mcp

mcpmcp-server
Seamlessly discover, set up, and integrate MCP servers with AI clients.
mcpmcp-server enables users to discover, configure, and connect MCP servers with preferred clients, optimizing AI integration into daily workflows. It supports streamlined setup via JSON configuration, ensuring compatibility with various platforms such as Claude Desktop on macOS. The project simplifies the connection process between AI clients and remote Model Context Protocol servers. Users are directed to an associated homepage for further platform-specific guidance.
- ⭐ 17
- MCP
- glenngillen/mcpmcp-server

mcp
Universal remote MCP server connecting AI clients to productivity tools.
WayStation MCP acts as a remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, enabling seamless integration between AI clients like Claude or Cursor and a wide range of productivity applications, such as Notion, Monday, Airtable, Jira, and more. It supports multiple secure connection transports and offers both general and user-specific preauthenticated endpoints. The platform emphasizes ease of integration, OAuth2-based authentication, and broad app compatibility. Users can manage their integrations through a user dashboard, simplifying complex workflow automations for AI-powered productivity.
- ⭐ 27
- MCP
- waystation-ai/mcp

manim-mcp-server
MCP server for generating Manim animations on demand.
Manim MCP Server allows users to execute Manim Python scripts via a standardized protocol, generating animation videos that are returned as output. It integrates with systems like Claude to dynamically render animation content from user scripts and supports configurable deployment using environment variables. The server handles management of output files and cleanup of temporary resources, designed with portability and ease of integration in mind.
- ⭐ 454
- MCP
- abhiemj/manim-mcp-server

OpenMCP
A standard and registry for converting web APIs into MCP servers.
OpenMCP defines a standard for converting various web APIs into servers compatible with the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling efficient, token-aware communication with client LLMs. It also provides an open-source registry of compliant servers, allowing clients to access a wide array of external services. The platform supports integration with local and remote hosting environments and offers tools for configuring supported clients, such as Claude desktop and Cursor. Comprehensive guidance is offered for adapting different API formats including REST, gRPC, GraphQL, and more into MCP endpoints.
- ⭐ 252
- MCP
- wegotdocs/open-mcp
Didn't find tool you were looking for?