
JupyterMCP
Enable direct Claude AI integration with Jupyter Notebook via the Model Context Protocol.
Key Features
Use Cases
README
JupyterMCP - Jupyter Notebook Model Context Protocol Integration
JupyterMCP connects Jupyter Notebook to Claude AI through the Model Context Protocol (MCP), allowing Claude to directly interact with and control Jupyter Notebooks. This integration enables AI-assisted code execution, data analysis, visualization, and more.
⚠️ Compatibility Warning
This tool is compatible ONLY with Jupyter Notebook version 6.x.
It does NOT work with:
- Jupyter Lab
- Jupyter Notebook v7.x
- VS Code Notebooks
- Google Colab
- Any other notebook interfaces
Features
- Two-way communication: Connect Claude AI to Jupyter Notebook through a WebSocket-based server
- Cell manipulation: Insert, execute, and manage notebook cells
- Notebook management: Save notebooks and retrieve notebook information
- Cell execution: Run specific cells or execute all cells in a notebook
- Output retrieval: Get output content from executed cells with text limitation options
Components
The system consists of three main components:
- WebSocket Server (
jupyter_ws_server.py): Sets up a WebSocket server inside Jupyter that bridges communication between notebook and external clients - Client JavaScript (
client.js): Runs in the notebook to handle operations (inserting cells, executing code, etc.) - MCP Server (
jupyter_mcp_server.py): Implements the Model Context Protocol and connects to the WebSocket server
Installation
Prerequisites
- Python 3.12 or newer (probably also work with older versions, but not tested)
uvpackage manager- Claude AI desktop application
Installing uv
If you're on Mac:
brew install uv
On Windows (PowerShell):
powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"
For other platforms, see the uv installation guide.
Setup
-
Clone or download this repository to your computer:
bashgit clone https://github.com/jjsantos01/jupyter-notebook-mcp.git -
Create virtual environment with required packages an install
jupyter-mcpkernel, so it can be recognized by your jupyter installation, if you had one before.bashuv run python -m ipykernel install --name jupyter-mcp -
(optional) Install additional Python packages for your analysis:
bashuv pip install seaborn -
Configure Claude desktop integration: Go to
Claude>Settings>Developer>Edit Config>claude_desktop_config.jsonto include the following:json{ "mcpServers": { "jupyter": { "command": "uv", "args": [ "--directory", "/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/PARENT/REPO/FOLDER/src", "run", "jupyter_mcp_server.py" ] } } }Replace
/ABSOLUTE/PATH/TO/with the actual path to thesrcfolder on your system. For example:- Windows:
"C:\\Users\\MyUser\\GitHub\\jupyter-notebook-mcp\\src\\" - Mac:
/Users/MyUser/GitHub/jupyter-notebook-mcp/src/
If you had previously opened Claude, then
File>Exitand open it again. - Windows:
Usage
Starting the Connection
-
Start your Jupyter Notebook (version 6.x) server:
bashuv run jupyter nbclassic -
Create a new Jupyter Notebook and make sure that you choose the
jupyter-mcpkernel:kernel->change kernel->jupyter-mcp -
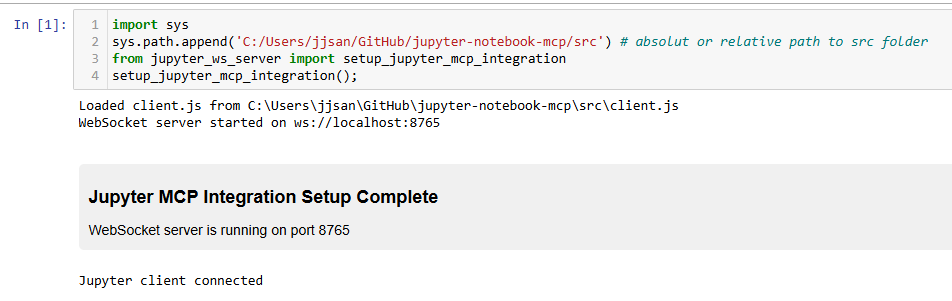
In a notebook cell, run the following code to initialize the WebSocket server:
pythonimport sys sys.path.append('/path/to/jupyter-notebook-mcp/src') # Add the path to where the scripts are located from jupyter_ws_server import setup_jupyter_mcp_integration # Start the WebSocket server inside Jupyter server, port = setup_jupyter_mcp_integration()Don't forget to replace here
'/path/to/jupyter-notebook-mcp/src'withsrcfolder on your system. For example:- Windows:
"C:\\Users\\MyUser\\GitHub\\jupyter-notebook-mcp\\src\\" - Mac:
/Users/MyUser/GitHub/jupyter-notebook-mcp/src/
- Windows:
-
Launch Claude desktop with MCP enabled.
Using with Claude
Once connected, Claude will have access to the following tools:
ping- Check server connectivityinsert_and_execute_cell- Insert a cell at the specified position and execute itsave_notebook- Save the current Jupyter notebookget_cells_info- Get information about all cells in the notebookget_notebook_info- Get information about the current notebookrun_cell- Run a specific cell by its indexrun_all_cells- Run all cells in the notebookget_cell_text_output- Get the output content of a specific cellget_image_output- Get the images output of a specific celledit_cell_content- Edit the content of an existing cellset_slideshow_type- Set the slide show type for cell
⚠️ DISCLAIMER
This is an experimental project and should be used with caution. This tool runs arbitrary Python code in your computer, which could potentially modify or delete data if not used carefully. Always back up your important projects and data.
Example Prompts
Ask Claude to perform notebook operations:
Python example
You can check the example notebook and the video demo
You have access to a Jupyter Notebook server.
I need to create a presentation about Python's Seaborn library.
The content is as follows:
- What is Seaborn?
- Long vs. Wide data format
- Advantages of Seaborn over Matplotlib
- Commonly used Seaborn functions
- Live demonstration (comparison of Seaborn vs. Matplotlib)
- Bar plot
- Line plot
- Scatter plot
For each concept, I want the main explanations provided in markdown cells, followed by one or more Python code cells demonstrating its usage. Keep the text concise—the cells shouldn't exceed 10 lines each.
Use appropriate slideshow types for each cell to make the presentation visually appealing.
Check Here the full conversation
Stata example
For this example, you need the Stata Software (v17 or later), which is not open source. If you already have Stata, you need to install the stata-setup package:
uv pip install stata-setup
Then, at the begining of your notebook, you need to additionally include:
import stata_setup
stata_setup.config('your_stata_installation_directory', 'your_stata_edition')
You can check the example notebook and the video demo
This exercise comes from Professor John Robert Warren webpage
You have access to a Jupyter Notebook server. By default it runs Python, but you can run Stata (v18) code in this server using the %%stata magic, for example:
%%stata
display "hello world"
Run the available tools to solve the exercise, execute the code, and interpret the results.
**EXERCISE:**
In this exercise, you will use data from the American Community Survey (ACS). The ACS is a product of the U.S. Census Bureau and involves interviewing millions of Americans each year. For an introduction to the ACS, visit the ACS website (here).
For this exercise, I have created a data file containing two variables collected from respondents of the 2010 ACS who lived in one of two metropolitan areas: Minneapolis/St Paul and Duluth/Superior. The two variables are: (1) People's poverty status and (2) the time it takes people to commute to work.
Use STATA syntax files you already have (from the first assignment or class examples) and modify them to accomplish the following goals.
1. Read the data file (`"./stata_assignment_2.dat"`) for this assignment into STATA.
2. Be sure to declare "zero" as a missing value for `TRANTIME`, the commuting time variable.
3. Create a new dichotomous poverty variable that equals "1" if a person's income-to-poverty-line ratio (`POVRATIO`) is less than 100, and "0" otherwise; see the bottom of the assignment for an example of how to do this in STATA.
4. Separately for Minneapolis/St Paul and Duluth/Superior, produce:
- a histogram of the commuting time (`TRANTIME`) variable.
- measures of central tendency and spread for commuting time.
- a frequency distribution for the poverty status (0 vs 1) variable.
5. Separately for Minneapolis/St Paul and Duluth/Superior, use STATA code to produce:
- a 95% confidence interval for the mean commuting time.
- a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of people who are poor. See below for an example of how to do this in STATA.
Use the results from step #4 above to:
6. Separately for Minneapolis/St Paul and Duluth/Superior, manually calculate:
- a 95% confidence interval for the mean commuting time.
- a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of people who are poor.
7. Confirm that your answers from steps #5 and #6 match.
Based on the results above, answer this question:
8. How do you interpret the confidence intervals calculated in steps #5 and #6 above?
9. Finally, create a do file (.do) with the all the Stata code and the answers as comments.
---
**DESCRIPTION OF VARIABLES IN "STATA ASSIGNMENT 2.DAT"**
**METAREAD** (Column 4-7)
Metropolitan Area
- `2240`: Duluth-Superior, MN/WI
- `5120`: Minneapolis-St. Paul, MN
**POVRATIO** (Column 18-20)
Ratio of person's income to the poverty threshold:
- `<100`: Below Poverty Line
- `100`: At Poverty Line
- `>100`: Above Poverty Line
**TRANTIME** (Column 21-23)
Travel time to work
- `0`: Zero minutes
- `1`: 1 Minute
- etc.
Check Here the full conversation
Testing with External Client
You can test the functionality without using Claude Desktop with the included external client:
uv run python src/jupyter_ws_external_client.py
This will provide an interactive menu to test some available functions.
For automated testing of all commands:
uv run python src/jupyter_ws_external_client.py --batch
Troubleshooting
- Connection Issues: If you experience connection timeouts, the client includes a reconnection mechanism. You can also try restarting the WebSocket server.
- Cell Execution Problems: If cell execution doesn't work, check that the cell content is valid Python/Markdown and that the notebook kernel is running.
- WebSocket Port Conflicts: If the default port (8765) is already in use, the server will automatically try to find an available port.
Limitations
- Only supports Jupyter Notebook 6.x
- Text output from cells is limited to 1500 characters by default
- Does not support advanced Jupyter widget interactions
- Connection may timeout after periods of inactivity
License
Other Jupyter MCPs
This project is inspired by similar MCP integrations for Jupyter as:
Star History
Repository Owner
User
Repository Details
Programming Languages
Join Our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest AI tools, news, and offers by subscribing to our weekly newsletter.
Related MCPs
Discover similar Model Context Protocol servers

QGISMCP
Integrate QGIS with Claude AI via Model Context Protocol
QGISMCP connects QGIS to Claude AI through the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling seamless two-way communication between the GIS platform and the AI assistant. It features a QGIS plugin that sets up a socket server and a dedicated MCP server for processing commands, facilitating tasks such as project manipulation, layer management, and Python code execution directly from Claude. This integration empowers users to streamline project creation, layer loading, and advanced automation within QGIS through AI-driven interaction.
- ⭐ 691
- MCP
- jjsantos01/qgis_mcp

Dune Analytics MCP Server
Bridge Dune Analytics data seamlessly to AI agents via a Model Context Protocol server.
Dune Analytics MCP Server provides a Model Context Protocol-compliant server that allows AI agents to access and interact with Dune Analytics data. It exposes tools to fetch the latest results of Dune queries and execute arbitrary queries, returning results in CSV format. The server is easily deployable, supports integration with platforms like Claude Desktop, and requires a Dune Analytics API key for operation.
- ⭐ 31
- MCP
- kukapay/dune-analytics-mcp

MCP Server for Data Exploration
Interactive Data Exploration and Analysis via Model Context Protocol
MCP Server for Data Exploration enables users to interactively explore and analyze complex datasets using prompt templates and tools within the Model Context Protocol ecosystem. Designed as a personal Data Scientist assistant, it facilitates the conversion of raw data into actionable insights without manual intervention. Users can load CSV datasets, run Python scripts, and generate tailored reports and visualizations through an AI-powered interface. The server integrates directly with Claude Desktop, supporting rapid setup and seamless usage for both macOS and Windows.
- ⭐ 503
- MCP
- reading-plus-ai/mcp-server-data-exploration

MCP Jira Server for Claude Code
A full-featured Model Context Protocol server for integrating Jira with Claude Code.
Provides a comprehensive MCP server enabling seamless integration of Jira functionalities with Claude Code. Supports issue management, sprint operations, comments, attachments, batch processing, and agile workflows via a standardized protocol for model context. Designed for secure, environment-based configuration and optimized for both individual and batch operations within Jira.
- ⭐ 5
- MCP
- tom28881/mcp-jira-server

Modbus MCP Server
Standardizes Modbus data for seamless AI integration via the Model Context Protocol.
Modbus MCP Server provides an MCP-compliant interface that standardizes and contextualizes Modbus device data for use with AI agents and industrial IoT systems. It supports flexible Modbus connections over TCP, UDP, or serial interfaces and offers a range of Modbus tools for reading and writing registers and coils. With customizable prompts and structured tool definitions, it enables natural language-driven interactions and analysis of Modbus data within AI workflows. The solution is designed to ensure interoperability and easy configuration within MCP-compatible environments.
- ⭐ 18
- MCP
- kukapay/modbus-mcp

youtube_mcp
YouTube transcription server with Model Context Protocol integration.
youtube_mcp is a server that enables transcription of YouTube videos using the Model Context Protocol (MCP). Users can set up the server, authenticate via an MCP key, and stream video transcript data for integrated AI tools. Designed for use with applications like Claude desktop, it supports OpenAI APIs and utilizes browser cookies for access.
- ⭐ 26
- MCP
- format37/youtube_mcp
Didn't find tool you were looking for?