FastMCP LaTeX Server (tex-mcp)
A microservice for rendering LaTeX and templates to PDF via the Model Context Protocol.
Key Features
Use Cases
README
FastMCP LaTeX Server (tex-mcp)
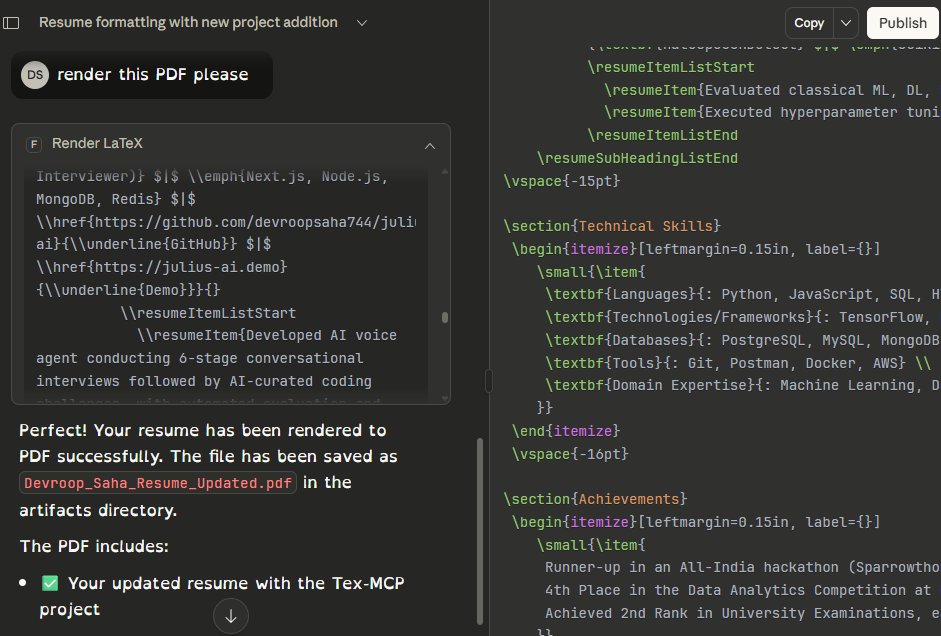
A small FastMCP-based Microservice that renders LaTeX to PDF. The server exposes MCP tools
to render raw LaTeX or templates and produces artifacts (a .tex file and .pdf)
under src/artifacts/.
This repository is prepared to run locally and to be loaded by Claude Desktop (via the
Model Context Protocol). The default entrypoint is run_server.py.
Demo
Quick features
- Render raw LaTeX to
.texand (optionally).pdfusing pdflatex - Render Jinja2 templates and compile to PDF
- Designed to run as an MCP server for Claude Desktop and other MCP-capable clients
Tools exposed by this MCP server
- Total tools: 5
- render_latex_document — write LaTeX and optionally compile to PDF
- render_template_document — render a Jinja2 template and optionally compile
- list_templates — list available templates
- list_artifacts — list files produced in
src/artifacts/ - get_template — return the raw contents of a template file so clients can inspect it before rendering
Getting started (local development)
Prerequisites
- Python 3.10+ (the project uses modern pydantic/fastapi stack)
- LaTeX toolchain (pdflatex) for PDF compilation (optional; if missing, server returns .tex only)
- Create a project virtualenv and install deps
Clone from GitHub
If you want to work from the canonical repository on GitHub, clone it first:
git clone https://github.com/devroopsaha744/TexMCP.git
cd TexMCP
After cloning you can follow the venv creation and install steps below.
python -m venv .venv
. .\\.venv\\Scripts\\Activate.ps1
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Run the server directly (stdio mode - used by Claude Desktop)
. .\\.venv\\Scripts\\Activate.ps1
python .\\run_server.py
# or run the venv python explicitly if you don't activate
.# .venv\\Scripts\\python.exe run_server.py
If run in stdio mode the server will speak MCP over stdin/stdout (this is what Claude Desktop
expects when it spawns the process). If you prefer HTTP, edit run_server.py and switch the
transport to http (see commented code) and run via uv run or uvicorn.
- Artifacts
Rendered outputs are placed in src/artifacts/. For each job you should see a .tex file and
— if pdflatex is available — a matching .pdf.
Templates
- Several example templates live in
src/mcp_server/templates/. There are 15 templates included (for examplesample_invoice.tex.j2,sample_letter.tex.j2,sample_resume.tex.j2). Uselist_templatesto get the full list programmatically. The templates are deliberately simple and ready to customize — add your own.tex.j2files to that folder to expand the catalog.
Included templates (in src/mcp_server/templates/)
default.tex.j2(base example template)sample_invoice.tex.j2sample_invoice2.tex.j2sample_letter.tex.j2sample_report.tex.j2sample_resume.tex.j2sample_presentation.tex.j2sample_certificate.tex.j2sample_coverletter.tex.j2sample_poster.tex.j2sample_thesis.tex.j2sample_receipt.tex.j2sample_recipe.tex.j2sample_poem.tex.j2sample_cv.tex.j2
Integration with Claude Desktop (quick)
Recommended: use the fastmcp CLI installer which will set things up to run from the project directory and use the project venv.
From your project root (with the venv already created and deps installed):
fastmcp install claude-desktop run_server.py --project C:\\Users\\DEVROOP\\Desktop\\tex-mcp
This ensures uv runs inside the project directory and uses the project's environment. After the installer runs, fully quit and restart Claude Desktop.
Manual Claude Desktop config
If you edit Claude's config yourself (Windows: %APPDATA%\\Claude\\claude_desktop_config.json), add a single server entry that points to the project Python executable. Example (replace paths if needed):
{
"mcpServers": {
"FastMCP-LaTeX-Server": {
"command": "C:\\\\Users\\\\DEVROOP\\\\Desktop\\\\tex-mcp\\\\venv\\\\Scripts\\\\python.exe",
"args": [
"C:\\\\Users\\\\DEVROOP\\\\Desktop\\\\tex-mcp\\\\run_server.py"
],
"cwd": "C:\\\\Users\\\\DEVROOP\\\\Desktop\\\\tex-mcp",
"transport": "stdio"
}
}
}
Notes
- Do NOT point Claude at the virtualenv
activatescript — it is a shell helper and not an executable. Point Claude to thepython.exeinside the venv (or touv.exeinside the venv if you installeduv). - After any config changes, fully restart Claude Desktop.
Docker
This project includes a Dockerfile so you can run the MCP server in a container.
Build (no LaTeX):
docker build -t fastmcp-latex:latest .
Build with LaTeX (larger image):
docker build --build-arg INSTALL_TEX=1 -t fastmcp-latex:with-tex .
Run (HTTP mode exposed on port 8000):
docker run -p 8000:8000 --rm --name fastmcp-latex fastmcp-latex:latest
Notes
- The container sets
MCP_TRANSPORT=httpby default. Inside the container the server binds to0.0.0.0:8000. - If you want to run the server in
stdiomode in a container you can override the env var:
docker run -e MCP_TRANSPORT=stdio ...
Artifact persistence
- To persist rendered artifacts on the host, bind mount the
src/artifactsdirectory:
docker run -p 8000:8000 -v $(pwd)/src/artifacts:/app/src/artifacts fastmcp-latex:latest
You can Use a Model Context Protocol / FastMCP client library (Like OpenAI Responses API) in your agent code to call tools programmatically. For example, in Python you can use the mcp or fastmcp client (see library docs) to connect to http://localhost:8000/mcp and call render_latex_document with arguments.
Security notes
- If you expose the HTTP endpoint beyond localhost, secure it (TLS, firewall, or authentication) — rendering arbitrary LaTeX can pose risks (shell commands in templates, large resource use).
Contributing
Thanks for wanting to contribute! See CONTRIBUTING.md for the development workflow, commit style, and how to open issues and pull requests.
License
This project is released under the MIT License — see LICENSE.
Star History
Repository Owner
User
Repository Details
Programming Languages
Tags
Topics
Join Our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest AI tools, news, and offers by subscribing to our weekly newsletter.
Related MCPs
Discover similar Model Context Protocol servers

PDF Tools MCP
Comprehensive PDF manipulation via MCP protocol.
PDF Tools MCP provides an extensive suite of PDF manipulation operations using the Model Context Protocol framework. It supports both local and remote PDF tasks, such as rendering pages, merging, extracting metadata, retrieving text, and combining documents. The tool registers endpoints through the MCP protocol, enabling seamless server-based PDF processing for various clients. Built with Python, it emphasizes secure handling and compatibility with Claude Desktop via the Smithery ecosystem.
- ⭐ 31
- MCP
- danielkennedy1/pdf-tools-mcp

Typst MCP Server
Facilitates AI-driven Typst interactions with LaTeX conversion, validation, and image generation tools.
Typst MCP Server implements the Model Context Protocol, enabling AI models to interface seamlessly with Typst, a markup-based typesetting system. It provides tools for tasks such as converting LaTeX to Typst, validating Typst syntax, listing and retrieving Typst documentation chapters, and rendering Typst code as images. The server is compatible with MCP agent clients, such as Claude Desktop and VS Code’s agent mode. All functionalities are exposed as tools for ease of LLM integration.
- ⭐ 79
- MCP
- johannesbrandenburger/typst-mcp

QR Code Generation MCP Server
Generate customizable QR codes from text via an MCP-compliant server.
Provides a server for generating QR codes from text input using the Model Context Protocol (MCP), supporting multiple transport modes such as STDIO, HTTP, and SSE. Allows customization of QR code appearance with options for color, style, and encoding settings. Outputs QR codes as base64 strings for easy integration or direct use in applications. Designed for compatibility with platforms like Claude Desktop and deployments using Docker or direct Python API usage.
- ⭐ 11
- MCP
- 2niuhe/qrcode_mcp

Jotdown
MCP Server for Notion Page Creation and mdBook Generation
Jotdown is an MCP server enabling large language models to interact seamlessly with Notion and generate markdown books (mdBooks). It allows LLMs to create or update Notion pages and manage the entire process of markdown book creation, including structure and navigation. Leveraging the Model Context Protocol, it provides tools for consistent and intelligent context handling between LLMs and external content platforms.
- ⭐ 19
- MCP
- Harry-027/JotDown

piapi-mcp-server
TypeScript-based MCP server for PiAPI media content generation
piapi-mcp-server is a TypeScript implementation of a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that connects with PiAPI to enable media generation workflows from MCP-compatible applications. It handles image, video, music, TTS, 3D, and voice generation tasks using a wide range of supported models like Midjourney, Flux, Kling, LumaLabs, Udio, and more. Designed for easy integration with clients such as Claude Desktop, it includes an interactive MCP Inspector for development, testing, and debugging.
- ⭐ 62
- MCP
- apinetwork/piapi-mcp-server

Google Workspace MCP Server
Full natural language control of Google Workspace through the Model Context Protocol.
Google Workspace MCP Server enables comprehensive natural language interaction with Google services such as Calendar, Drive, Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Slides, Forms, Tasks, and Chat via any MCP-compatible client or AI assistant. It supports both single-user and secure multi-user OAuth 2.1 authentication, providing a production-ready backend for custom apps. Built on FastMCP, it delivers high performance and advanced context handling, offering deep integration with the entire Google Workspace suite.
- ⭐ 890
- MCP
- taylorwilsdon/google_workspace_mcp
Didn't find tool you were looking for?